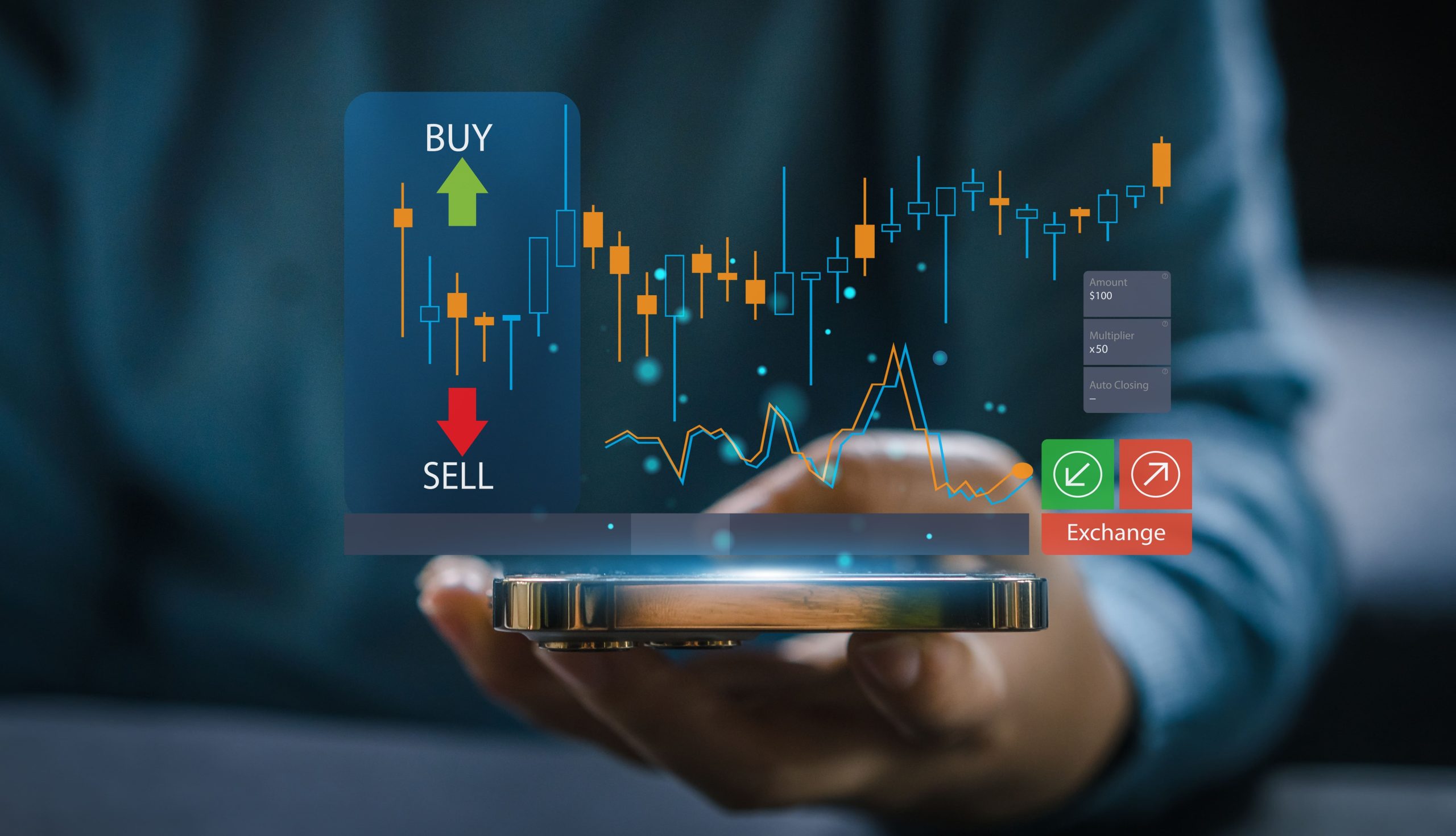
Forex trading, or foreign exchange trading, is the global marketplace for buying and selling currencies. It is one of the largest financial markets in the world, with a daily trading volume exceeding $6 trillion. The forex market offers vast opportunities for traders, but it also requires a deep understanding of how it works to succeed بروکرهای فارکس با پشتیبانی فارسی.
What is Forex Trading?
Forex trading involves the exchange of one currency for another, often in the form of currency pairs. The most popular currency pairs include EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar), GBP/USD (British Pound/US Dollar), and USD/JPY (US Dollar/Japanese Yen). Unlike other financial markets such as stocks or commodities, forex markets are decentralized, meaning trading happens directly between parties without a central exchange.
The goal of forex trading is to profit from the price fluctuations between two currencies. For example, if a trader buys the EUR/USD pair at a rate of 1.2000, and the price moves up to 1.2500, the trader can sell the pair and make a profit from the price difference.
Key Components of Forex Trading
- Currency Pairs: Currencies are traded in pairs because you are buying one currency while selling another. There are two main types of currency pairs:
- Major Pairs: These pairs include the most traded currencies globally, such as EUR/USD, GBP/USD, and USD/JPY.
- Minor Pairs: These pairs involve currencies from smaller economies, such as the Australian Dollar (AUD) or Canadian Dollar (CAD).
- Leverage: Leverage allows traders to control a larger position than they could with just their available capital. For example, with 100:1 leverage, a trader can control $100,000 with only $1,000. While leverage can amplify profits, it also increases the risk of significant losses.
- Bid/Ask Spread: The bid price is the price a buyer is willing to pay for a currency, while the ask price is the price a seller is asking for. The difference between these two prices is called the spread, which is how brokers make money.
- Pip: A pip (percentage in point) is the smallest price movement that a currency pair can make. For most currency pairs, a pip is equivalent to 0.0001 of the exchange rate. Understanding pips is crucial to calculating potential profits and losses in a trade.
- Trading Hours: The forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week. It opens on Sunday evening and closes on Friday night. Trading is continuous, with various financial centers around the world, such as London, New York, and Tokyo, taking turns to drive market activity.
How to Start Forex Trading
- Education and Research: Before diving into forex trading, it’s essential to educate yourself about the market’s basics, technical analysis, and trading strategies. Many brokers and educational platforms offer free resources, courses, and webinars.
- Choose a Reliable Broker: Selecting a reputable forex broker is a critical step in your trading journey. Ensure the broker is regulated by recognized authorities, offers competitive spreads, and provides reliable trading platforms such as MetaTrader 4 or 5.
- Start with a Demo Account: Most brokers offer demo accounts where you can practice trading without risking real money. This is an excellent way for beginners to familiarize themselves with the market and trading platform.
- Develop a Trading Plan: A trading plan includes your goals, risk tolerance, and strategies. It’s important to stick to your plan and not let emotions guide your decisions. Many successful traders use technical analysis and charting tools to predict market trends.
- Risk Management: Proper risk management is vital in forex trading. Always use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses, and never risk more than a small percentage of your trading capital on a single trade.
Strategies for Successful Forex Trading
- Trend Following: This strategy involves identifying the direction of the market and trading in the same direction. Traders use technical indicators like moving averages to help spot trends.
- Range Trading: Range trading is based on the idea that currency prices will stay within a defined range for a period of time. Traders buy at support levels and sell at resistance levels, profiting from price fluctuations within the range.
- Breakout Trading: Breakout traders aim to identify key support or resistance levels and place trades when the price breaks through these levels. This strategy is often used during times of high market volatility.
- Scalping: Scalping involves making multiple small trades throughout the day to capture small price movements. This strategy requires quick decision-making and fast execution, and it can be quite risky.
Risks Involved in Forex Trading
While forex trading offers the potential for high returns, it also comes with significant risks. The market’s volatility can lead to substantial gains, but it can also cause large losses. Factors like geopolitical events, economic data releases, and central bank policies can influence currency prices in unexpected ways.
To mitigate these risks, traders must use proper risk management techniques, such as setting stop-loss orders, diversifying their portfolio, and trading with a clear plan.